Good for business. Good for people and planet.
The SDG Impact Standards are management standards designed to guide businesses and investors to embed sustainability and the SDGs at the core of their internal management and decision-making practices – and have the confidence they are doing so in a holistic and systematic way.
They provide the framework to support organizations to make better decisions by placing sustainability and the SDGs at the heart of value creation and central to purpose. They guide businesses and investors to decide which impacts are important and relevant. This in turn informs organizations on how those impacts should be managed. When there is insufficient data to make a decision, the SDG Impact Standards can guide organizations on managing risks. They also help to align incentives across an organization, ensuring governance practices reinforce commitments and intent.
They guide organizations to reimagine business models and partnerships to innovate, create solutions and reach underserved stakeholders, involving them in decision-making.
Learn more about the SDG Impact Standards.
For information in French click here.
The SDG Impact Standards build on and complement existing work undertaken by others on impact management and measurement. In fact, in many ways the SDG Impact Standards provide a decision-making framework to make sense of the existing principles, frameworks and tools. It also fills knowledge gaps in current market practices which are undermining progress towards sustainability and the achievement of the SDGs.
All four sets of the SDG Impact Standards follow the same structure. This enables a shared language and approach for sustainability, the SDGs and impact management, making it easier to connect different industry players across the economic system. This lays the groundwork for an enabling environment for greater cross-sector collaboration and innovation in SDG financing solutions.
The below diagram illustrates how the SDG Impact Standards sit as the core decision-making framework that bring in high-level principles, existing and future frameworks and supporting resources.
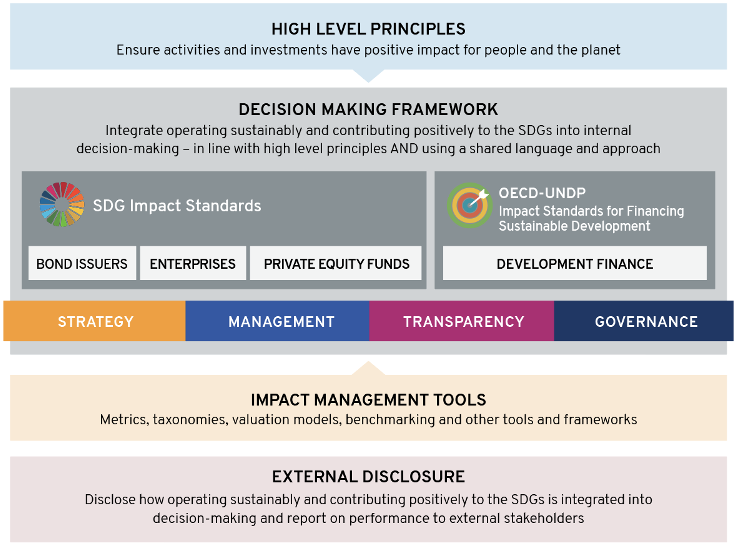
Source: UNDP and OECD
The SDG Impact Standards are aligned with a number of high level principles, including:
Implementing the SDG Impact Standards should ensure alignment with the relevant high-level principles as well. The SDG Impact Standards generally go further than the high-level principles, providing additional guidance on operationalizing the high-level principles, and filling gaps in management practice and decision-making not covered by the high-level principles.
The SDG Impact Standards require the implementation of several existing core decision-making frameworks, including: UN Guiding Principles for Business and Human Rights
Other decision-making frameworks that are aligned with the SDG Impact Standards, may help organizations meet the requirements of the SDG Impact Standards, for example:
The SDG Impact Standards do not dictate which IMM tools to use, but rather provide guidance on how organizations can select from existing and future tools available and apply them effectively to help make better decisions. Such tools may include metrics, taxonomies, valuation models, benchmarking tools e.q. IRIS+, GRI, UNCTAD metrics, Voluntary National Reviews (VNRs) on the implementation of the SDGs, SDG Impact Market Intelligence Investor Maps, Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) to the Paris Accord, Blab SDG Action Manager and UNEP FI Impact Analysis Tools.
On the basis that external reporting should be a summary of managements’ decisions, implementing the SDG Impact Standards will help organizations be prepared to meet their current and future regulatory disclosures and external reporting requirements of other stakeholders. This includes whether these requirements are on a full well-being, also known as, double materiality basis or on a more limited financial materiality basis. For instance, preparing for EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting (CSRD) or International Sustainability Standards Boards (ISSB) requirements, preparing reports based on Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), the Sustainable Development Goal Disclosure Recommendations or using the Integrated <IR> Reporting Framework.
The SDG Impact Standards define the requirements for a sound management practice that places sustainability and the SDGs at the core of value creation: Strategy, Management Approach, Transparency and Governance.
These four core elements increase the likelihood that an organization is operating sustainably and contributing positively to the SDGs. Taken together, they support organizations to make better decisions for people, planet and profit.
The core elements are based on contributing positively to sustainable development and achieving the SDGs. This can only be done by demonstrating respect for human rights, planetary boundaries and other responsible business practices. This in turn is realized through effective impact management and decision-making.
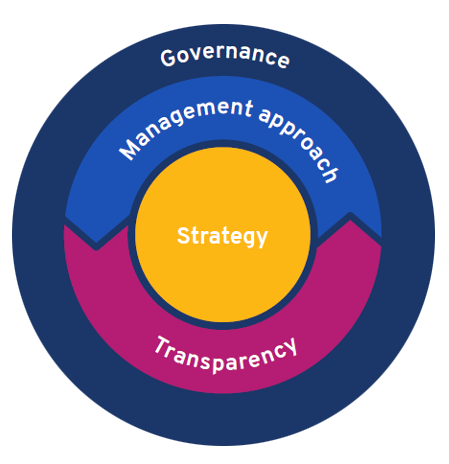
Standard 1 (Strategy): Embedding sustainability and the SDGS in purpose and strategy is important because it drives attention, focus and resources to what matters most and where the organization can have the most significant impact on important outcomes - including by reducing negative ones.
Standard 2 (Management Approach): Integrating responsible business practices and managing for impact into organizational systems and decision-making helps organizations generate options and make more informed choices between options to optimize their contribution towards sustainability and achievement of the SDGs. Operating responsibility and sustainably and contributing to the achievement of the SDGS is not an add on to what business gets done, it's how all business is done.
Standard 3 (Transparency): Being transparent is an important element of being accountable to Stakeholders - all interested parties including those affected or potentially affected in the future by the organization's decisions and activities. It also helps Stakeholders make more informed decisions, for instance about whether they want to work with or for the organization, invest in or lend to the organization, or buy or use the organization's products and services.
Standard 4 (Governance): Governance is an essential element of embedding responsible business and managing for impact practices into organizational decision-making. The organization's informal and formal governance mechanisms define expectations of behavior, how decisions are made and how the organization holds itself accountable for its decisions and actions in accordance with its values, principles and policies.
Get ready:
For documents in other languages, see Resources page
Take action:
The SDG Impact Assurance Scheme will strengthen impact integrity and promote market trust and credibility in the claims made by businesses and investors about their sustainability and impact management practices.
The SDG Impact Assurance Scheme is based on the SDG Impact Standards, but with minimum requirements set at lower level to encourage participation and continuous improvement towards best practice in line with the SDG Impact Standards over time.
The SDG Impact Assurance Scheme is being designed to meet the conformity assessment requirements of ISO 17065 (Conformity assessment – Requirements for bodies certifying products, processes and services).
The SDG Impact Seal will provide a market signal to distinguish organizations who are more likely to be operating sustainably and contributing positively to the SDGs, based on their internal sustainability and impact management practices.
Learn more about the SDG Impact Assurance Design and Implementation Working Group here.
Sustainable Development Goals © 2021 SDG Impact Terms and Conditions